This guide covers everything you ever wanted to know about gynecomastia and male breast surgery – but were too embarrassed or afraid to ask.
What is Gynecomastia?
“Gynecomastia” comes from the Greek word “gyne”, which means woman, and “mastos”, which is the Greek word for breasts.
Gynecomastia is the abnormal development or swelling of breast tissue in males, which may result from a hormonal imbalance between the quantity of estrogen and testosterone produced by the body.
The condition is most commonly seen in pubescent boys and middle-age to elderly men. As males age, their testosterone is increasingly converted to estrogen. This gradual decrease of testosterone accounts for hormone-induced gynecomastia cases in adult men. It can occur to one breast or both, be localized primarily behind the nipple and areola, or involve the entire pectoral area.
For men who suffer from gynecomastia, the condition can detrimentally impact their ability and desire to participate in everyday life. As New York-based plastic surgeon Dr. Mordcai Blau explains, “I remember a patient once saying to me, ‘It’s a beautiful day and I can’t enjoy it. I can’t take off my shirt in the pool, at the beach or any other public places.’ For many men, gynecomastia is both a social and physical problem.”
Psychologically gynecomastia can be devastating, especially during adolescence, and can influence people’s social lives.
But there’s more than just the embarrassment factor that makes gynecomastia so unpleasant. It’s not uncommon for men with the condition to experience intense pain in their breasts as well, similar to what some women experience during their menstrual cycle. The combination of pain, social and physical discomfort the condition brings with it leaves a lot of men feeling embarrassed and insecure about their masculinity.
For men with more minor variations of the condition, gynecomastia may recede without the need for surgery, which is commonly the case with pubescent males. But if you have noticed puffiness or drooping around the breast, or feel uncomfortable with the feminine appearance of your chest, it may be worth consulting with your doctor to see what options are available to you.

RELATED: Brandon Liberati’s Gynecomastia Journey
What Causes Male Breast Enlargement?
Gynecomastia can be caused by a range of factors. Recognizing the causation of the condition is imperative, as it may indicate the presence of a more serious health condition, such as a testicular tumor. Careful medical evaluation can determine the best way to address the problem and proceed with treatment.
These are the main factors that doctors believe leads to the condition:
Natural Hormonal Changes
Estrogen and testosterone are responsible for the development and preservation of sexual traits in all genders. Testosterone is responsible for male characteristics like body hair and muscle mass, while estrogen is responsible for female characteristics, among them enlarged breasts.
Many people don’t realize that men produce estrogen as well, just in significantly smaller quantities than women. Gynecomastia can result when these two hormones are imbalanced for any number of reasons. This imbalance usually happens during one of three preeminent stages of growth:
- Infancy: Over 50% of male infants are born with enlarged breasts because of prolonged exposure to their mother’s estrogen. This swelling eventually subsides after a few weeks.
- Puberty: It is very common for pubescent males to develop gynecomastia because of the significant hormonal changes taking place in their bodies at that age. Some enlargement of male breast tissue often occurs during puberty, with the incidence of noticeable pubertal breast enlargement said to be as high as 60%. For most young men this is temporary, but for others the breast tissue proliferation will persist, and occasionally even keep growing. The condition usually goes away after a few months, but if swelling or other symptoms persist for more than six months, it’s a good idea to bring it to the attention of a physician.
- Middle-age and older: As men age they produce less testosterone and more estrogen, which can create an hormonal imbalance that results in gynecomastia. Sometimes the symptoms are so slight that men don’t even realize they suffer from the condition. It is important to note that breast cancer can also be present in men with gynecomastia, although it is highly unlikely for males under the age of 70.
Steroids and Certain Medications
Gynecomastia can also be the side effect of certain drugs and medications, namely among bodybuilders and other athletes who use hormone-based performance enhancers.
According to professional bodybuilder, board certified plastic surgeon, and gynecomastia expert Dr. Rick Silverman, “Anabolic steroids that are most commonly associated with gynecomastia are those which undergo aromatization, or conversion to estrogen-like compounds, a process which takes place in fat and muscle cells. These estrogens cause a shift in that ratio, leading to growth of the breast tissue. The testosterones and anadrol are common culprits, but some of the other testosterone derivatives can be responsible as well.”
The following medications have been known to cause gynecomastia.
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Chemotherapy specific to cancer patients
- Anabolic steroids and androgens
- AIDS medications. Gynecomastia sometimes develops in HIV-positive men receiving a treatment called highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).
- Anti-anxiety medications (Diazepam, Ativan, etc.)
- Antiandrogens that treat prostate enlargement, prostate cancer and other diseases/disorders
- Some over-the-counter antibiotics
- Some ulcer medications
- Some heart medications
Recreational drugs
Animal studies have shown that exposure to the active ingredient in marijuana can result in a decrease in testosterone levels, a reduction of testicular size, and abnormalities in the form and function of sperm. Although the association between marijuana and gynecomastia hasn’t been conclusively proven, it appears very plausible.
Alcohol abuse, amphetamines, and opiates (Hydrocodone, heroin, Methadone, Percocet) are also believed to be contributing factors.
Various health conditions
The following conditions have been linked to gynecomastia in some individuals:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Kidney disease
- Obesity
- Tumors
- Malnutrition
- Liver failure and cirrhosis
- Hypogonadism, or atrophy of the testes
Diagnosing Gynecomastia: Signs and Symptoms
In addition to the obvious drooping puffy nipples or enlarged breasts, there are several other signs to look for when determining if you have gynecomastia. In some cases, only one breast will enlarge. This is known as unilateral gynecomastia. In other cases, both breasts will enlarge. The fatty tissue may be primarily localized behind the nipple and areola or involve the entire pectoral area.
The following is a short list of symptoms that may indicate that you suffer from gynecomastia:
- Swollen breast gland tissue
- Breast tenderness
- Puffy nipples
- Nipple discharge in one or both breasts
Pseudogynecomastia vs Gynecomastia
Male breast enlargement isn’t always caused by a hormonal imbalance. Pseudogynecomastia may present similar symptoms to gynecomastia, but the causes and treatments for these two conditions are quite different.
Pseudogynecomastia is basically male breast enlargement from fat deposits, whereas gynecomastia is caused by glandular enlargement.
With pseudogynecomastia, the individual suffers from an excess of adipose tissue, possibly due to poor physical fitness or obesity. This adipose tissue is soft to touch, and generally associated with significant weight gain later in life. Should you ever find yourself diagnosed with pseudogynecomastia, however, you can take comfort in the knowledge that a little liposuction will usually be all that is needed to address the condition. In some cases, it can be treated with diet and exercise.
With gynecomastia, the individual has excess breast gland tissue, which has a harder texture. Blood tests and mammograms are also generally administered to confirm or negate any initial suspicions of gynecomastia. If the results are conclusive or inconclusive for any reason then additional testing will be done, which could include CT scans, MRI scans, testicular ultrasounds, and tissue biopsies. These tests are usually taken to determine if gynecomastia has been misdiagnosed, or to ensure more severe problems like breast cancer are not present.
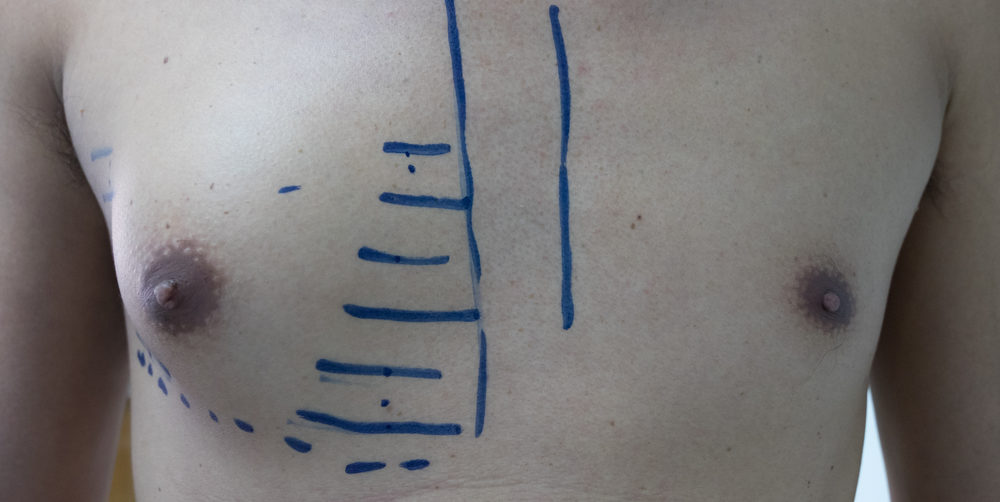
Gynecomastia Grades: From Mild to Severe
Gynecomastia can come in all shapes and sizes, from being barely noticeable to something painful and virtually impossible to hide. Most grading systems rate the severity of the condition from 1 to 4, with 4 being the most severe, while others use a more granular approach, adding 2 or even 3 extra levels of severity.
Type 1
Type 1 gynecomastia produces puffy nipples, and is more common among men with a leaner build. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia.
Type 2
Approximately 90% of excess glandular tissue in Type 2 patients can be removed through surgery. Liposuction may also be performed.
Type 3
In Type 3 cases, the breasts protrude from the chest at a 45-60 degree angle. Surgery is required to remove the excess tissue.
Type 4
Type 4 gynecomastia is characterized by sagging skin and breast tissue protruding from the chest at an angle of 60-90. Surgery is performed to remove the excess breast tissue, and also to excise the excess skin due to chest sag.
Type 5
Sagging breast tissue that falls below the chest fold is tightened through a procedure known as the “anchor lift.” Excess skin requires surgical removal.
Type 6
Type 6 is characterized by extreme sag of the breast tissue that falls below the chest fold, extending under the armpits and towards the patient’s back. Surgical removal and liposuction are required to flatten the breast and remove fatty deposits.
Type 7
This is the most extreme stage of gynecomastia, with severe sagging and noticeable volume in the breast (up to DD cup size). Surgical removal of excess breast tissue is required.
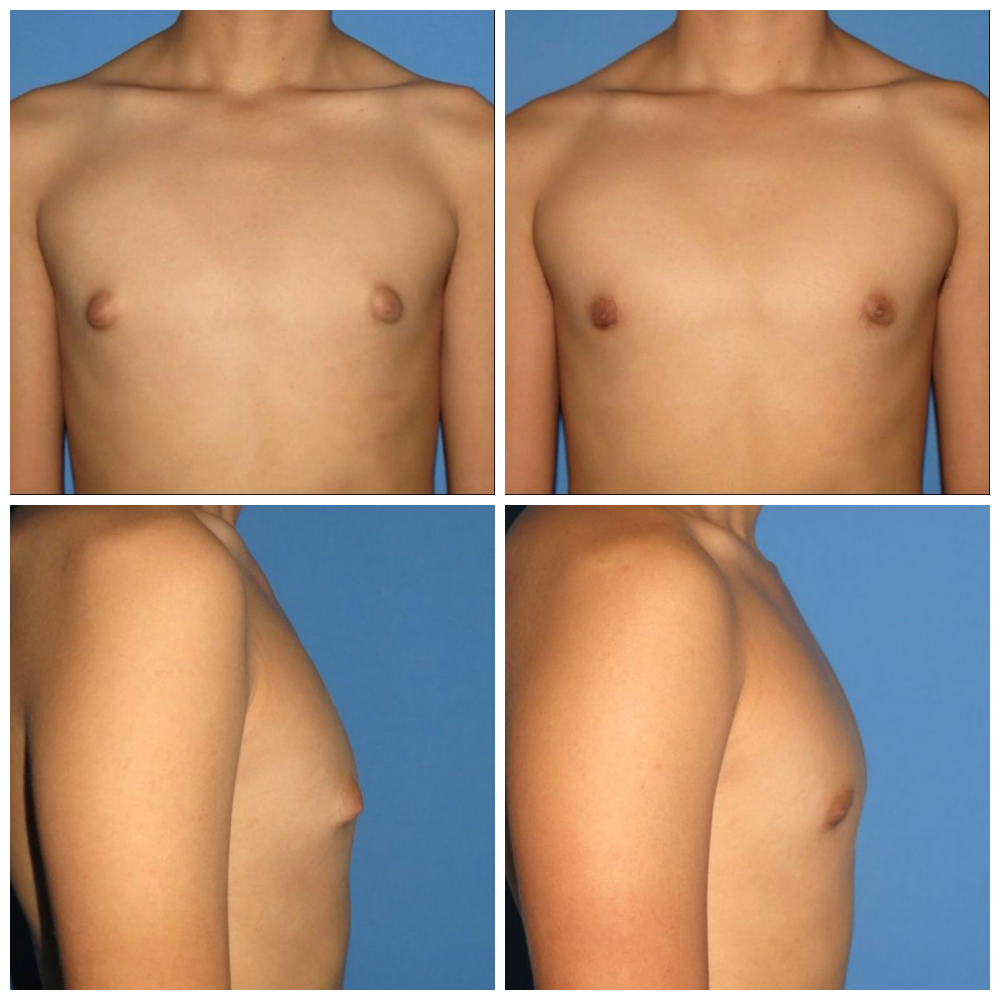
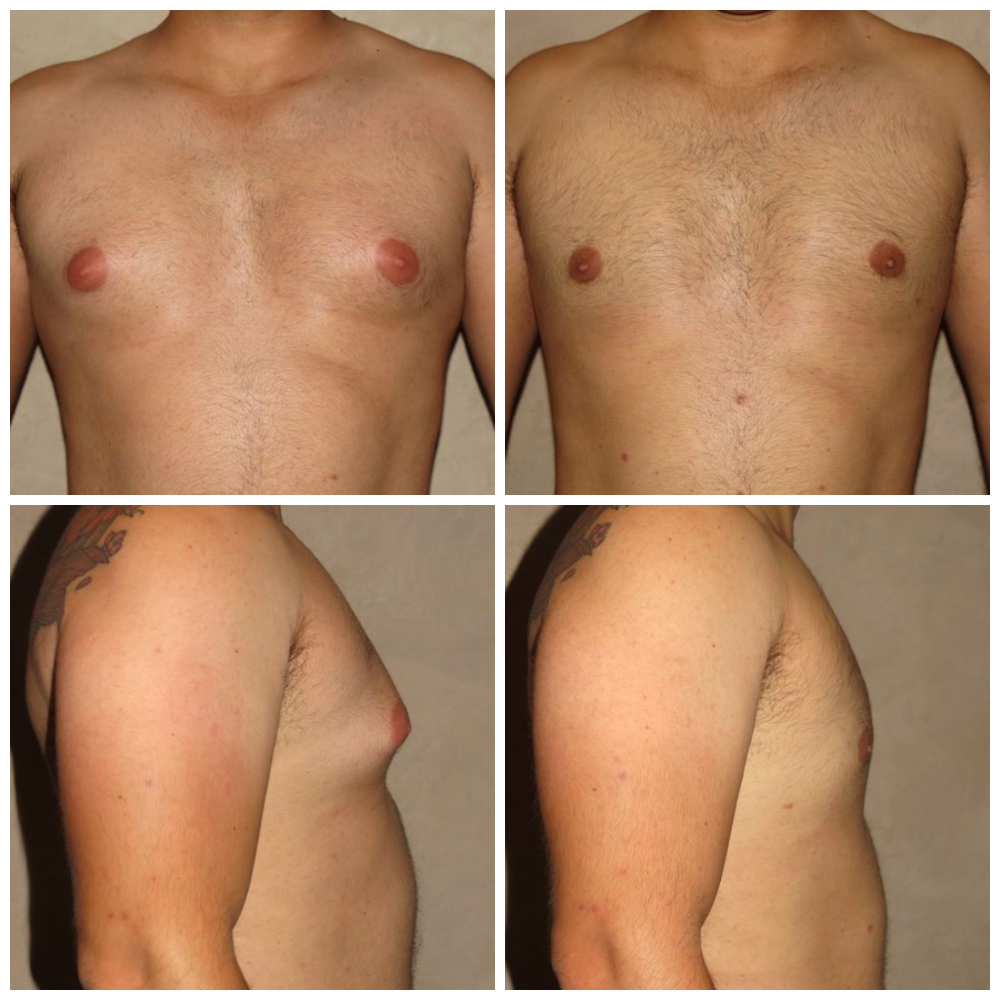
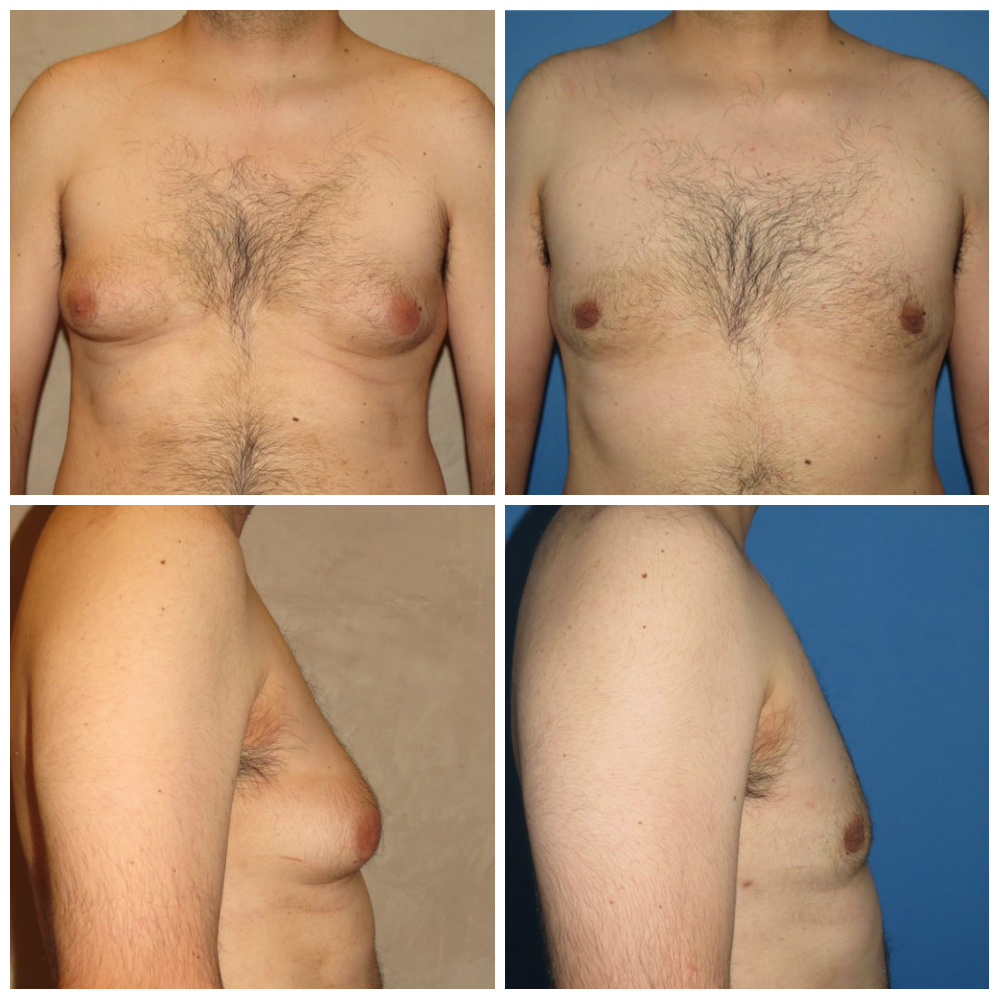
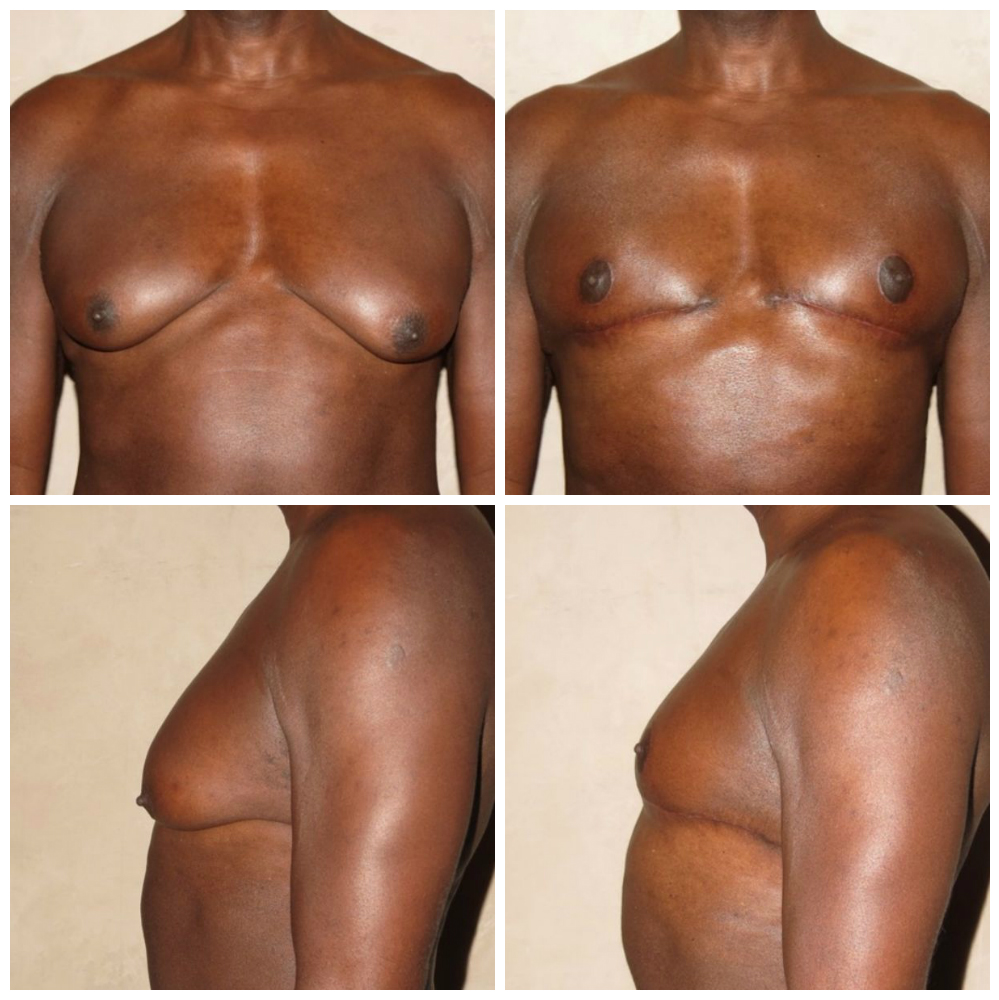
Choosing a Plastic Surgeon You Can Trust
Selecting a certified member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) is very important. The ASPS is recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS), which has been approving medical specialty boards since 1934.
By choosing a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons to carry out your gynecomastia reduction surgery, you can be assured that you’re in the hands of a qualified, highly-trained plastic surgeon. All ASPS member surgeons must meet the following rigorous standards before being accredited certification:
- Complete at least six years of surgical training following medical school, with a minimum three years of plastic surgery residency training
- Pass comprehensive oral and written exams
- Graduate from an accredited medical school
- Complete continuing medical education, including patient safety, every year
- Perform surgery in accredited, state-licensed, or Medicare-certified surgical facilities
Don’t let yourself become confused by other official sounding groups. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons is the largest plastic surgery specialty organization in the world. Founded in 1931, it represents 94% of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States.
RELATED: Plastic Surgeon vs. Cosmetic Surgeon — What’s the Difference?
How Much Does Gynecomastia Surgery Cost?
Male breast reduction surgery costs can vary widely. According to statistics from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), in 2014 the average cost of gynecomastia reduction surgery in the United States was roughly $3,000-$3,500.
However, that price doesn’t necessarily include anesthesia, operating room facilities or other related expenses. Once everything is factored in, the final tally will likely be closer to $6,000 or $7,000 as the following need to paid for:
- Anesthesia fees
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Medical tests
- Post-surgery garments
- Prescription medications
- Surgeon’s fee
Prices can also depend on a surgeon’s level of experience, the actual procedure required, and where in North America they’re located. So it’s definitely not cheap, but also not so expensive to be priced entirely out of range for most Americans.
And remember, if these costs are a little more than you can handle all at once, many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans for these procedures, so be sure to ask your surgeon about payment options.
Gynecomastia Surgery and Health Insurance
Unfortunately, most health insurance plans do not cover the correction of gynecomastia. That being said, insurance policies vary greatly so it is still worthy of investigation.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons has published a position paper for physicians and insurers that defines the recommended criteria for reconstructive cases of gynecomastia. You can ask your doctor for a copy and submit it to your insurer. The ASPS firmly believes that people fitting the following qualifications should routinely be covered by their health insurance policies:
- Men whose condition can’t be corrected through any other medical treatments
- Men who are physically healthy and of relatively normal weight, with no life-threatening illnesses or medical conditions that could impair healing
- Non-smokers and non-drug users
- Men whose breast development has stabilized
- Men bothered by their breasts being too large
Sometimes adolescents can also benefit from surgery, although secondary procedures will likely be required in the future should breast development continue.
Preparing for Your First Consultation
When going to your first gynecomastia surgery consultation be prepared to discuss the following with your doctor:
- Your goals for surgery
- All of your medical conditions, drug allergies and/or medical treatments you are presently undergoing
- Any medications you take regularly: prescription drugs, steroids, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco, or recreational drugs like cannabis, cocaine, or opiates.
- Any prior surgeries you have undergone.
Your doctor might also choose to:
- Evaluate your general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Request a copy of your medical records
- Discuss your options and recommend a course of treatment
- Discuss likely outcomes of gynecomastia correction and any potential complications
- Discuss the type of anesthesia he/she feels is appropriate for your surgery
- Perform diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia, including the testing of your endocrine function
- Examine your breasts, taking detailed measurements of their size and shape, skin quality, and the placement of your nipples and areolas
In the days leading up to your surgery, your doctor might ask you to:
- Go for lab testing or undergo a medical evaluation
- Start taking certain medications or adjust the medications you’re currently taking
- Stop smoking
- Avoid taking aspirin, any anti-inflammatories or herbal supplements as they can increase bleeding
The success and safety of your specific gynecomastia procedure very much relies on you being honest and candid during your consultation. Be prepared to answer questions about your health, expectations, and overall lifestyle, and ask the surgeon anything you are unsure about.
Checklist: Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Am I a good candidate for this procedure?
- What will be expected of me to get the best results?
- Where and how will you perform my procedure?
- What surgical technique is recommended for me?
- Are you certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery?
- Were you trained specifically in the field of plastic surgery?
- How many years of plastic surgery training have you had?
- Do you have hospital privileges to perform this procedure? If so, at which hospitals?
- Is the office-based surgical facility accredited by a nationally- or state-recognized accrediting agency, or is it state-licensed or Medicare-certified?
- How long of a recovery period can I expect, and what kind of help will I need during my recovery?
- What are the risks and complications associated with my procedure?
- How are complications handled?
- What are my options if I am dissatisfied with the outcome of my surgery?
- Do you have before-and-after photos I can look at for this procedure
- What results can I reasonably expect?
(Source: ASPS)
Your Gynecomastia Surgery: Step by Step
The intended result of male breast surgery is to reduce breast size and all redundant breast tissue with the ultimate goal being to enhance the contours of the chest. Gynecomastia surgery should reduce or eliminate any physical discomfort associated with the condition, not to mention finally rid patients of the emotional dissatisfaction and/or embarrassment gynecomastia has caused them.
Your gynecomastia reduction surgery (GRS) will likely take place in either an accredited, office-based surgical facility or a hospital. These surgeries are almost always performed on an outpatient basis. Try to make sure you have somebody who can drive you to and from your surgery and ideally stay with you for at least your first night after surgery. Although complications are highly unlikely, you should still do your best to follow the surgeon’s recovery guidelines.
For men with Type 7 gynecomastia or a particularly large amount of redundant breast tissue, more than one procedure might be required. These staged procedures, however, can also have their benefits, primarily because they sometimes result in less scarring and diminished recovery times.
Surgery is performed in three steps.
1. Anesthesia
Anesthetic options include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Depending on the type of gynecomastia being treated, your surgeon will recommend the best option for you. General, intravenous and local anesthesia are all at times used for male breast reduction surgery. However, the anesthetic you will be given will be based upon the severity of your condition and the procedure your plastic surgeon has determined most suitable for you.
2. Liposuction
In cases where enlarged breasts are primarily the result of excess fatty tissue, tumescent liposuction alone will most likely be used. This involves the insertion of a cannula — essentially a thin, hollow tube – through several small incisions. The cannula is then moved back and forth in a controlled motion to loosen any excess fat, which is subsequently removed from the body by vacuum suction.
For mild to moderate gynecomastia, specific types of liposuction cannulas are often used in conjunction with direct removal of excess breast glandular tissue through these small incisions. Other specific techniques can reduce the areola when required, or reposition the nipple to create the appearance of a more natural contour.
There are a few different liposuction techniques your doctor can choose to remove any excess fat resulting from gynecomastia. He or she will discuss the technique they feel is most appropriate for your situation prior to surgery.
3. Excision
Excision is recommended when glandular breast tissue or excess skin must be removed to correct gynecomastia. Excision is also required when the areola must be reduced or the nipple repositioned to reflect a more natural male contour. Excision patterns will vary depending on your surgeon’s preference and the specifics of your case.
RELATED: Zwivel’s Complete Guide to Liposuction
Male Breast Surgery Risks and Safety
As with any surgical procedure, there’s always some element of risk. Realistically, you can rest assured that there are considerably riskier ordeals than a relatively simple operation to treat gynecomastia. Nevertheless, you should always be aware of potential complications that may occur before undergoing any type of surgery.
These are some of the risks you should be aware of before agreeing to gynecomastia reduction surgery:
- Potential allergic reactions to tape, suture materials, glues, topical preparations or injected agents
- General anesthesia risks, as with any surgical procedure requiring anesthesia
- Hematoma (localized collection of blood outside of the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue)
- Blood clots
- Breast asymmetry, contour or shape irregularities
- Changes in nipple and/or breast sensation (be it temporary or permanent)
- Temporary or permanent damage to deeper structures like nerves, blood vessels, muscles, and lungs
- Deep vein thrombosis, cardiac and pulmonary complications
- Death of breast fatty tissue (also known as fat necrosis)
- Seroma (excess fluid accumulation)
- Infection
- Persistent pain
- Poor wound healing and visible scarring
- The need for revision surgery
These risks and any others specific to your situation should be fully discussed with your doctor prior to giving your consent for surgery. Even if the risks involved are rare and relatively minor, if you have a concern, speak up and ask questions.
For instance, your surgeon might not be able to deliver optimal results with only one surgery. A follow up surgery might be necessary to treat any potential complications from the initial surgery, or to address any additional tightening or repositioning of the breasts that could be required.
You should make sure you understand all aspects of the surgical procedure about to be performed on you. It’s perfectly normal to feel some anxiety about it all, whether it’s just excitement about your new look or the result of preoperative stress. Don’t be timid when it comes to discussing any potential insecurities you may have with your plastic surgeon.
What to Expert After Surgery
For the first few weeks following your surgery you can typically expect to see some swelling, bruising, and a diminished feeling in your chest and nipples. The vast majority of symptoms will gradually subside over a few weeks, and any permanent scarring from gynecomastia surgical procedures is minimal.
Immediately After Surgery
- Painkillers will help with any potential discomfort, along with an antibiotic to prevent infection from occurring.
- Bandages will be applied to your incisions and a support garment possibly employed to help minimize any swelling that occurs while supporting your new chest contour as it heals.
- In some instances, a small thin tube might temporarily be placed under the skin to drain any excess blood or fluids that could collect.
- Ensure your surgical incisions aren’t subjected to any excessive force, swelling, abrasion, or intense motion throughout the period you are healing.
- Your doctor will provide you with any specific instructions you’ll need on how best to care for the surgical site and drains, as well as which medications to apply in order to aid with the healing process and reduce the potential for infection.
- Pay attention to any significant shortness of breath or unusual, irregular heart beats. The chances of anything like this happening are very slight, however, should you experience either of these symptoms it could indicate something of a more serious nature, so be sure to notify your surgeon.
Long-Term Recovery
- Avoid participating in sports or any form of strenuous exercise for roughly one month post-op. Recovery will take between 3 to 6 months, although the amount of recovery time required tends to vary from patient to patient.
- Avoid drugs and steroids that could cause the condition to return.
- Be diligent in maintaining a stable, healthy weight.
Partial results of surgical procedures are immediately visible and with time any post-surgical swelling will resolve and the incision lines generally fade. The final results become fully visible over the period of a few months. Any surgical treatment to correct gynecomastia will involve incisions, and while most of these incision lines are concealed within natural contours, there’s a possibility that some may be visible.
There’s simply no question your new upper-body is going to enhance your self-image and confidence. This factor alone motivates many men to consider surgery. The relief gained from being able to bare the chest in public and shower after gym class without self-consciousness is prized by many men.

RELATED: Top Plastic Surgery Procedures for Men
Latest Techniques and Scientific Studies
In the December 2016 issue of the Annals of Plastic Surgery, several surgeons outlined a breakthrough in gynecomastia reduction referred to as the “Orange Peel Excision” technique. What is unique about this excision method is that the gland is excised as one, long piece of tissue in a method similar to an orange being peeled (following a corkscrew shape).
This approach overcomes the weaknesses of existing gynecomastia reduction surgery – such as long scars, lengthy surgical times, the risk of hematoma and contour abnormalities – as the gland can be excised via one short incision and removed completely, promising safer and aesthetically improved results for patients along with a shorter downtime.
The liposuction pull-through technique has been utilized by many surgeons as one of the safest and most effective methods of performing gynecomastia reduction surgery. However, a recent study published in the April 2017 issue of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery reported success with further refining and enhancing this approach. Surgeons performed the surgery as an outpatient procedure on 52 patients without general anesthesia by making only one incision above the inframammary fold. Excess glandular tissue was removed by excision and liposuction.
The study reported successful outcomes among patients, with no drains needed following surgery, and no reported complications such as fluid accumulation beneath the skin, hematoma (bruising or blood accumulation beneath the skin) or nipple distortion. However, it is important to note that this approach works most effectively on patients who do not suffer from significant skin excess.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gynecomastia caused by?
Gynecomastia is a disorder of the endocrine system that creates a swelling of the male breast tissue. It can affect one or both breasts, and stems from testosterone and estrogen hormonal imbalances.
The condition is mainly found in infants, adolescent boys and older men. Accordingly to the Mayo Clinic, the prevalence of gynecomastia peaks between the ages of 50 and 80 as a result of normal changes in hormone levels — at least 1 in 4 men in this age group are affected. It can also be the side effect of certain drugs and medications, namely among bodybuilders and other athletes who use hormone-based performance enhancers.
Are there home remedies or pills available to combat gynecomastia?
Sure, tons of them. But perhaps the more relevant question is “do any of them actually work?”
Although a number of estrogen-blocking drugs are sold as cures for gynecomastia, none are approved for that purpose by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Beware of modern day snake oil salesmen hawking pills and other miracle cures alleged to “cure” gynecomastia. To date, there is no legitimate evidence suggesting there is any efficacy whatsoever to these alleged cures. While it’s true that adult gynecomastia might go away if left untreated and once one’s hormones start to stabilize and balance out, it’s rare.
Can diet and exercise alone reduce breast size for men with gynecomastia?
Once you’ve been diagnosed with full blown gynecomastia, no amount of exercise will revert your chest back to it’s former masculine glory. In fact, sometimes exercise can actually make the condition appear even worse because as the chest muscle gets stronger and fuller it pushes the glandular tissue out, which in turn makes the pointiness, or feminine appearance of the chest, that much more noticeable.
If, however, you learn your “gynecomastia” is purely the result of extreme weight gain, diet and exercise could be considered an option. This because the ailment you’re really dealing with here is pseudogynecomastia, not true gynecomastia, hence the different way it is treated.
So surgery is the only option, then?
Surgery remains the most effective treatment for male breast enlargement.
The procedure’s popularity has surged in recent years. In 2015, men made up 40% of breast reduction surgeries (a 35% growth in the past 15 years), according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
There are two types of cosmetic surgery for gynecomastia: one is liposuction, which targets excess breast fat tissue while leaving the underlying breast tissue intact. The other is mastectomy, which involves the removal of breast gland tissue through small incisions over the side of the breast, in the underarm or near the areola.
It requires a masterful surgeon to remove the excess fat and glandular tissue. Explaining the procedure in layman’s terms, Dr. Gilbert Lee, a triple board-certified plastic surgeon in San Diego says, “This surgical procedure is most often performed using liposuction. In extreme cases, skin can be removed as well. Because the fat is permanently removed from the area, the results are permanent. The result is a flatter, firmer and more contoured chest.”
What techniques do doctors most commonly employ in gynecomastia surgery?
The most common technique surgeons employ is to first make a peri-areolar incision to remove the glandular tissue. They then typically use liposuction around the area to create definition. Occasionally doctors will choose only liposuction to treat the condition.
This approach, however, has also been known to leave unsatisfactory results as glandular tissue is still left behind. Should your doctor inform you this is their preferred approach, be sure to have them explain exactly why they’ve come to this conclusion.
Is male breast reduction surgery expensive?
As with all plastic surgery procedures, final costs can vary significantly depending on your surgeon, his/her level of experience, and where in the country they are located. In the United States the average price for surgical procedures to treat gynecomastia done is roughly $6,000-$7,500 in total.
It’s highly recommended that you do some shopping around before settling on any one practitioner. Not only so you find the best price, but because you also want to feel good about the plastic surgeon you decide upon. Remember, you can proceed fully confident that any board-certified plastic surgeon you choose will be competent and capable of performing the surgery you require.
Is gynecomastia surgery ever covered by health insurance?
While unlikely, it all depends on your health insurer and plan. Different insurers have different policies when it comes to gynecomastia. It’s probably wise not to count on everything being covered by your health insurance plan, but it’s still definitely something worth looking into. After all, the position of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) is that Type 2 Gynecomastia and up should definitely be covered by health insurance.
As a general rule, however, the chances of your insurer covering the cost of gynecomastia treatments are greatly improved if the following conditions are applicable:
- You have pain in your chest area, shoulders, back, upper back and/or neck
- You have undergone diagnosis by a qualified physician who has certified you are suffering from discomfort and pain as a result of the condition
- Your diagnosis confirms there is abnormality with the only valid recourse being surgery
- The condition has affected your daily functions and led to physical and physiological problems
- You are able to present all the paperwork and documents required
Are there any medical conditions that could prevent me from undergoing surgery?
While highly unlikely, there are some serious medical conditions that could cause your doctor some concern. Severe heart disease, malignant hyperthermia or any particularly intense bleeding disorders are all potential reasons why a surgeon might identify you as an unsuitable candidate for surgery.
What blood tests are done prior to surgery?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a prerequisite for most surgical patients. A “PT/PTT” might possibly be requested to test your clotting mechanism if you’ve been regularly taking any aspirin-containing medications or certain types of vitamins/supplements.
Can gynecomastia turn into cancer?
According to the Mayo Clinic, having gynecomastia may slightly increase your risk of male breast cancer due to the change in ratio of estrogen to testosterone in your body.
While breast cancer is uncommon in men, it happens. Enlargement of one breast or the presence of a firm nodule indicates that you could have male breast cancer.
Is there a maximum age limit for patients considering gynecomastia surgery?
No. The only thing would be if you have any age-related medical conditions that could possibly compromise your health as a result of the surgery. If this were to be determined your surgeon could be hesitant to proceed or simply decline to perform the surgery altogether.
Am I too young to have gynecomastia surgery?
Possibly. Under most circumstances doctors will recommend that you wait until you are at least 18 years old before undergoing this type of surgery. But there can be exceptions to this rule, which is something for your doctor to determine.
Is there anything in particular I need to do to prepare for surgery?
Absolutely. Your doctor will likely insist you not smoke cigarettes for at least 2 weeks prior to surgery and not start up again for another 4 weeks after that. You’ll be informed not to take Ibuprofen or any drugs that could promote excessive bleeding.
Among the non-medicinal or herbal products to also avoid for the same reason are Fish and Flax Seed Oils, St. John’s Wort, Ginko Biloba or excessive amounts of Vitamin E. As a rule of thumb, you’ll be strongly advised to avoid all non-crucial medications, supplements or vitamins for at least 2 weeks prior to surgery and another two weeks post-operation.
Dr. Rick Silverman is a Boston-based board-certified plastic surgeon who specializes in diseases of the breast in both men and women. He has also written several articles on the treatment of gynecomastia in bodybuilders, and gives these pre-surgery suggestions to his patients:
• Medication or supplements that can cause excessive bleeding such as aspirin or fish oil should be avoided.
• Some patients are encouraged to lose weight prior to surgery.
• Smokers should quit. For routine gynecomastia surgery, this is less critical than those cases which require skin removal, where smoking can compromise blood supply to delicate skin flap.
• Shaving is not required except around the incision site, on the nipple in most cases, unless extensive skin removal is required.
• Gym rats can work out up until the day of surgery.
Will I be required to stay in the hospital overnight?
No. Male breast reduction surgery is almost always a same-day outpatient procedure requiring no more than 3 hours to complete.
Directly after surgery you will be taken to a recovery area where a nurse will monitor your condition for another 60-90 minutes. Once it’s determined that you’re stable you’ll be able to return home, although it’s advised you have a friend or family member escort you and ideally keep an eye on you for the next 24 hours or so, just in case there are complications.
How much recovery time will I need following surgery?
Patients are usually up and mobile less than 24 hours after surgery. Most will have some discomfort in the early post-operative period and may use a narcotic for pain relief for a few days, and then at bedtime for a few more days to help with sleep, but rarely do they experience significant pain past a week.
Essentially, you’ll be looking at an initial 7 – 10 days recovery time immediately after surgery, and if drains were used they’ll probably be left for roughly 3 days before being removed at your first post-op appointment. While recovery periods vary from patient to patient based on a wide variety of factors, the average recovery time is 3 – 6 months, at which point most patients will have fully healed – although it can take a few months longer for scars to fade to the point where they’re no longer visible.
For the first 45 days post-operation you’ll need to avoid any especially strenuous activities, in particular anything involving your upper body like weightlifting or working out at the gym. Some doctors will advise their patients to wear a compression garment for the first 45 days following surgery.
What are drains and why do some doctors use them when others don’t?
Some doctors just don’t feel drains are necessary for this type of procedure so these decisions are made on a case by case basis, partially depending on the doctor and the type/level of gynecomastia compromising the patient. Drains help to reduce swelling and promote better skin condition post-operation by enabling fluids underneath the skin to collect into a small bottle, which is easily emptied by the patient.
Essentially drains prevent these fluids from collecting inside the body, which then would have to be drained by other means.
What’s a compression vest? Will I need to wear one and if so, for how long?
It’s sometimes necessary to wear a compression vest for a month to six weeks following surgery. This is because once the gland is excised and liposuction performed, a large open space exists, so compression garments (like a vest) help the tissue come together and close properly.
Another thing the garments do is help reduce any initial swelling over the surgical site. Again, this is decided on a case by case basis. Sometimes doctors will choose an ACE bandage over a vest, while other times a little gauze dressing will do the trick.
Will I be in pain after surgery and if so, for how long?
The long-acting local anesthesia you’ll have been given will be effective for roughly one full day. When it wears off, most patients report experiencing moderate discomfort for another 24 hours or so before it starts to fade, although some patients say they still feel mild soreness from the liposuction and around the surgical site for another day or two after that.
Just in case you fall into the latter category, take comfort in the knowledge that doctors typically prescribe plenty of pain medication for people recovering from gynecomastia surgery.
How soon will I be able to return to work?
Patients typically return to work 5 to 7 days after surgery, depending on what type of work they do. If your occupation requires a lot of physical labor it’s recommended you wait at least 7 – 10 days week before going back to work.
How about exercising?
Dr. Silverman stresses that all surgeons have their own approach. “I allow my patients to resume low-impact cardio activity after a week. They may resume weight training after two weeks, avoiding overhead maneuvers for the first week back, and no chest until a total of four weeks have passed.”
Within four to six weeks, nearly all patients are able to go back to all normal activities.
Will surgery result in any scarring?
Yes, regardless of the technique your surgeon chooses for your male breast reduction there will be some scarring afterward.
Board-certified Miami-based plastic surgeon Dr. Adam J. Rubinstein says scarring is one of the top reservations men have when considering gynecomastia surgery. Yet, there is no need to worry. While it’s impossible to predict the appearance of the scars, in most cases they’re barely apparent.
“In my experience, 80% of cases can be improved with liposuction alone. Liposuction leaves very small discrete scars about the size of a grain of white rice,” says Dr. Rubinstein. “In the other 20 percent of cases, a small incision is made along the edge of the areola to allow access to remove the excess abnormal tissue.” This scar follows a natural line and is barely visible when fully healed.
Are there any postoperative complications I should be aware of?
Complications are very, very rare. Excessive fluid can sometimes accumulate under the skin, and if a drain wasn’t used, this fluid will need to be aspirated with a needle. Also, if after two days you’re still feeling intense pain that isn’t helped by your prescribed medications, you should notify your doctor as this could indicate a problem.
The only other serious complication which could possibly occur is hematoma. Hematoma refers to a collection of blood underneath the skin. You will know this has happened should there be any excessive bruising, swelling, or pain, usually on just one side of the chest. If you suspect hematoma post-surgery, it’s crucial that you contact your doctor immediately.
Gynecomastia Testimomials
These testimonials from men who underwent gynecomastia surgery offer examples of how transformative the procedure can be.
“I was very uncomfortable with my appearance since adolescence. After being mistaken for a girl when I was maybe 13 or 14, I spent the next decade and a half always wearing loose clothing. I wore a sweatshirt to school all through high school.
Several years after college, I found out I could have surgery and did it. It was life-changing. I became comfortable with my appearance. I would imagine this is common for all sorts of appearance changes. The difference is, in my opinion, that a big nose or a giant mole may be unattractive but otherwise benign. Nobody questions your gender or renders an opinion on anything else other than that one thing.”
– R.V.
“I went through with the surgery just a few days ago. It was my first time under general anesthesia so I was a bit anxious about it, but the doctors and nurses were excellent and made me feel very comfortable. The surgery was over in an hour (I don’t remember a thing), and I was awake and out the door after 30-45 minutes of recovery from the anesthesia. They gave me diazepam and hydrocodone to reduce the pain and help me relax and sleep for this week while I recover.
The total cost of all appointments and my surgery was just under $6500. However, I can already state that it’s worth it. I still have some moderate swelling and some gnarly looking bruises, but the flatness of my chest is already 90% better! In a few weeks, I am going to get back into running to lean up and will work on more chest exercises once I’m fully healed. In the meantime, I have to wear a compression vest, which is moderately annoying but not too uncomfortable.
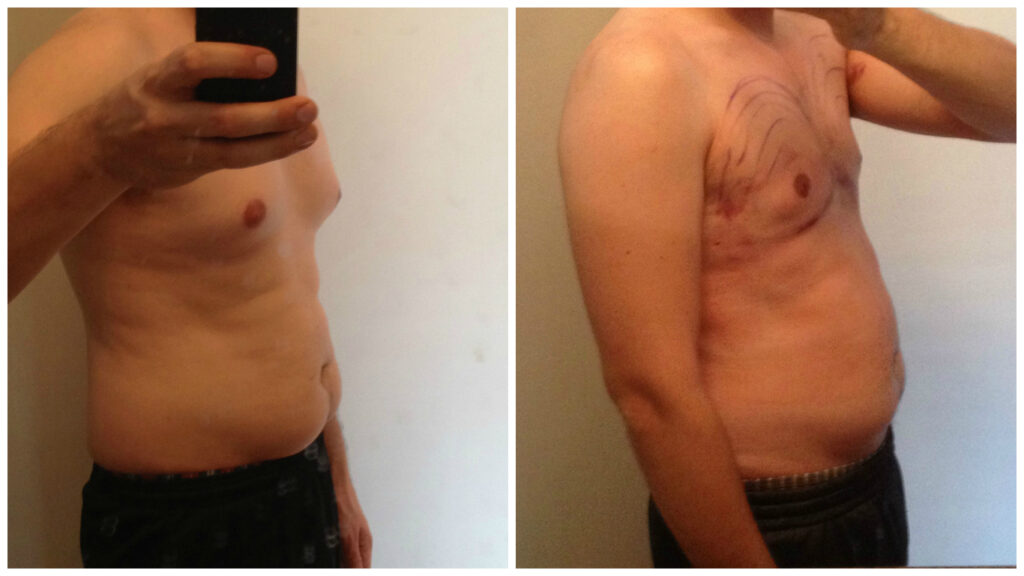
Even at this early stage post-surgery, I am very happy with my results. I would really encourage any guy dealing with gynecomastia issues to go see a doctor. In some cases, it can be addressed through hormonal treatments without surgery. Even if it requires surgery, I think it is worth it for the benefit of feeling comfortable in my body.”
– Tofur99 (source)
“After surgery it’s pretty surreal, taking the binder and under armor shirt off and seeing this flat small contoured chest staring back at me. My drive to lose all excess fat is very strong now, I’m already planning out the next year-15 months in terms of weight loss and muscle gain, feel so freed up now that I’m not having to work around the gyno, there’s no point in time where too much muscle or too little fat or any combination thereof will make me look ridiculous and self conscious anymore, it’s just full steam ahead.
My chest is just so damn flat, it’s changed the appearance of my whole upper body in a huge way, shirts hang so nicely off my shoulders that now the problem area is my stomach, which isn’t even that big.
I urge anyone who has gyno and is considering surgery to fu$*ing do it, scrape together the money, find the best gyno-specialized plastic surgeon you can and get it done. Life is too short not to, I’m 26 and wish I did this when I was 17-19. The self consciousness/low self esteem/lack of confidence never goes away.”
– Banmoobz