Quick Facts
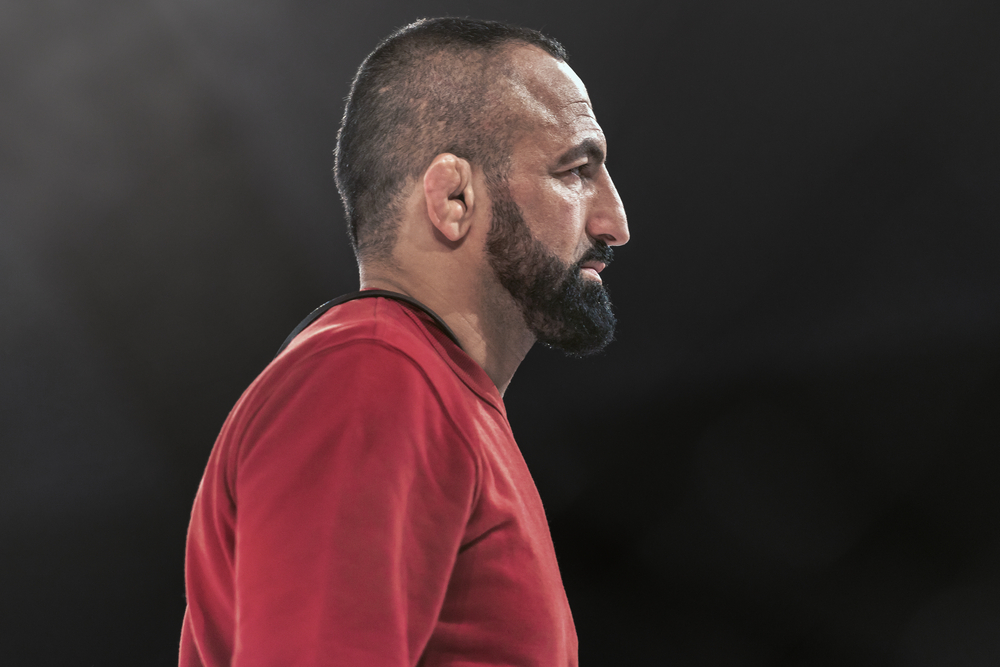
- Cauliflower ear, a deformity that results from blunt trauma, is common in people who participate in contact sports.
- If the injuries aren’t addressed soon enough, otoplasty may be required to improve the ear’s appearance.
- The best way to prevent cauliflower ear it is to wear protective headgear while participating in activities that put you at risk.
What is Cauliflower ear?
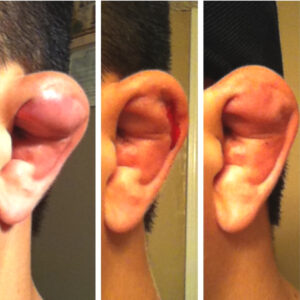
Cauliflower ear, also known as wrestler’s ear, is a condition that results in the pooling of fluid or blood between the skin and cartilage of the pinna (outer ear). The pinna is made up of a thin layer of skin that is tightly adhered to a framework of cartilage. As fluid separates the skin from the cartilage, the ear becomes deformed resembling the outer portion of a cauliflower.
What Causes Cauliflower ear?
Any impact significant enough to damage the blood vessels of your ear can cause cauliflower ear. People who participate in contact sports or who have been involved in an accident resulting in head trauma are at the highest risk of developing cauliflower ear.
What are the Symptoms of Cauliflower ear?
If you have recently experienced trauma to your ear, check to see if you have any swelling or bruising. Depending on the severity of the trauma, varying amounts of fluid may collect between the skin and cartilage of your ear. This fluid typically results in a number of common symptoms, such as:
- Bruising
- Redness
- Warmth
- Swelling
- A shriveled outer ear
- Paleness of your ear due to blood loss
- A change in the curvature of your ear
If left untreated, the fluid that collects in your ear can interrupt blood flow to healthy cartilage, resulting in more serious symptoms, such as:
- Hearing loss
- Ringing ears (tinnitus)
- Headaches/Migraines
- Vision changes
- Severe bleeding
- Facial swelling and bruising
- Necrosis of healthy cartilage
- Scarring (fibrous tissue)
Treatment Options for Cauliflower Ear
Any trauma or injury to the ear should receive early medical attention and intervention to prevent the development of cauliflower ear. Immediate interventions can include:
Ice to Reduce swelling
Following an ear injury accompanied by any of the previously listed signs and symptoms, you should ice the ear for periods of 15-20 minutes at a time until you reach the emergency department, which should ideally happen within 6 hours of the initial trauma.
Head and Neck Examination
Any severe trauma to the external ear requires a thorough examination of the head and neck to rule out more severe intracranial injury. As part of this process, the physician will use an otoscope to check the inner structures of the ear, including the tympanic membrane (ear drum) to ensure that it is intact and not punctured.
Draining the Auricular Hematoma
In order to prevent tissue death of the ear cartilage, the physician will need to drain the auricular hematoma, using one of these two techniques:
- Aspiration, if the hematoma is small or soft, can be done using an 18-gauge needle. Before draining, the physician will typically administer lidocaine and epinephrine to numb the area. After draining, the doctor will apply a compression dressing to facilitate healing and regrowth of healthy cartilage.
- Surgical incision can be done if the hematoma is large or firm, or if it has been more than 6 hours since the initial injury. Surgical draining can be considerably more involved than aspiration and may require local or general anesthesia. The incision can typically be made and hidden in an inconspicuous part of the ear. Following surgical draining, stitches will be required in addition to compression dressing.
Antibiotics
These will be prescribed orally in many cases to prevent infection. If no antibiotics are taken, it’s important to watch for any signs of infection, including pus near the site of injury, aspiration or incision.
The need for subsequent draining of an auricular hematoma is fairly common. So, it’s likely that patients will receive a referral to an otolaryngologist – also known as an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist – for continued management and to prevent development of cauliflower ear.
Surgical Correction
For patients who did not receive proper treatment within the ideal time frame following an ear injury, otoplasty or plastic surgery on the ear may be the only option. The goal of otoplasty for cauliflower ear is to correct the deformity to whatever extent is possible and return the ear to a more normal appearance.
The surgeon can employ a number of techniques to improve the appearance of cauliflower ear, such as making small, concealed incisions; excising (or cutting out) the fibrous tissue; and resculpturing, recontouring and/or shaving the remaining cartilage.
How to Prevent Cauliflower Ear
If you participate in any type of contact sport where injuries to the ear are common, you should always wear properly-fitted protective headgear. Invest in adequate protective equipment while participating in activities that may put you at risk for ear injuries.
If you do experience an ear injury, early intervention is the next best strategy to prevent the development of cauliflower ear.