- Botox is a preventative treatment for chronic migraines.
- It is suitable for patients who experience 15 or more headache days per month.
- Most people need a few treatment cycles before they see results.
- Many insurance companies will help cover the costs of treatment.
Everyone gets a headache every now and then. But for some, headaches are more than an occasional nuisance — they’re a debilitating health condition that has a significant impact on their quality of life.
Chronic migraines affect 1-2% of the population, according to research published in Cephalalgia. Conventional treatments typically include pain relievers, preventative medication, cognitive behavioral therapy and addressing risk factors such as obesity, depression and anxiety.
In addition to these treatments, Botox is also becoming an increasingly popular way of preventing chronic migraine headaches.
How does Botox help with chronic migraines?
The active ingredient in Botox is botulinum toxin type A, a neurotoxin typically used cosmetically to reduce the appearance of facial lines.
While Botox is usually employed to treat wrinkles, it can also help patients who regularly get headaches. In 2010, Botox was granted FDA approval for use in the treatment of chronic migraines.
Botox is considered a preventative treatment. It’s believed Botox alleviates migraines by preventing the release of chemicals that transmit pain signals. The exact mechanism is still not fully understood.
Are you a good candidate?
A wide range of people are able to achieve good results with Botox. You may be a suitable candidate if you are over the age of 18 and suffer from chronic migraines.
As noted in research published in Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, a chronic migraine is defined as having a headache on 15 or more days per month. Generally speaking, the more frequently you have headaches, the better you will respond to Botox, however, it is not recommended for people who experience fewer than 15 headache days a month.
It’s also important to note that Botox isn’t considered to be a first-line treatment for chronic migraines, so consult with your healthcare provider about other options before trying Botox. Antidepressants and anti-seizure drugs are commonly prescribed as preventative medication for chronic migraines. Some patients also find alternative treatments such as acupuncture and cognitive behavioral therapy to be effective.
>>Some patients who have tried multiple treatments, including botox, without success may opt to have migraine surgery
What is involved with the procedure?
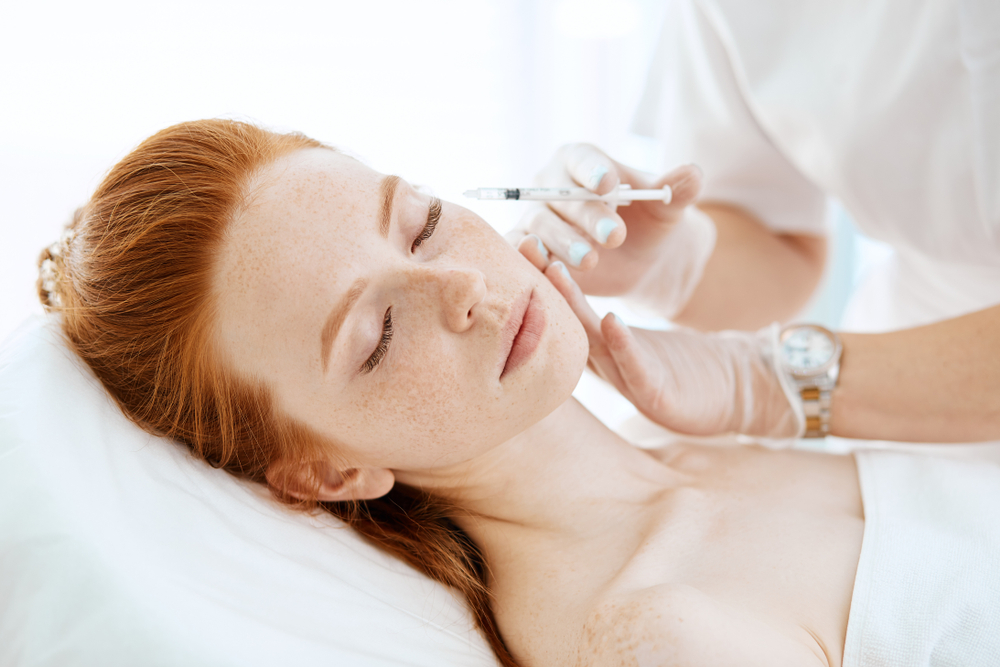
The Botox procedure to treat migraine headaches takes approximately 15 minutes to complete. Injections are given by a healthcare provider in your doctor’s office using very fine needles.
Before the injections, your provider will ask if you have any muscle tenderness. He or she will then examine your muscles and ask you to contract them prior to injection.
Next, your provider will begin injecting the Botox into 31 sites spread across seven head and neck muscle areas. A total of 155 units are used and distributed among the muscles as follows:
| Muscle | Number of Units |
|---|---|
| Corrugator | 10 |
| Procerus | 5 |
| Frontalis | 20 |
| Temporalis | 40 |
| Occipitalis | 30 |
| Cervical paraspinal | 20 |
| Trapezius | 30 |
Results/reviews
The effects of Botox are temporary, typically lasting approximately 12 weeks, which is one treatment cycle.
You may need to undergo a few treatment cycles before noticing a significant difference, but many patients say it’s worth the wait. Studies have shown that patients who receive five treatment cycles experience an average of 9.2 fewer headache days per month.
In other investigations, 61% of patients reported excellent pain relief and a further 20% reported some pain relief after being treated with Botox for chronic migraines. According to online reviews, 86% of patients say they would recommend this therapy to others.
>>Read more about a ‘Botox for migraines’ success story
What are the side effects of Botox chronic migraine treatment?
Botox is widely used around the world and considered to be a very safe treatment. As with any procedure, however, there are some risks to be aware of. As noted in research conducted at the University of Cologne, the most common adverse effects of Botox are:
- Neck pain
- Pain near the injection site
- Drooping eyelid
- Muscle weakness
You may also experience bruising around the injection site and flu-like symptoms. Contact your provider should you experience any concerning side effects or if your symptoms persist.
FAQ
Does Botox migraine treatment cause hair loss?
This may be a common concern, but there’s no evidence to suggest using Botox to treat chronic migraines causes hair loss. Rather, studies have indicated Botox could actually be useful for reducing hair loss.
How long does it last?
Approximately 3 months. You will need additional treatments should you wish to maintain results.
Is Botox suitable for preventing occasional headaches?
No. In this context Botox is designed to be used by people who suffer from chronic migraines and experience at least 15 headache days a month. It is not suitable for treating episodic migraines or tension headaches.
I didn’t feel any difference after my first treatment. Why is my body not responding?
It takes a while for the full results of Botox to take effect. Most people need to undergo a few treatment cycles before they see results. Many healthcare providers recommend trying at least three cycles before giving up.
How is Botox for chronic migraines different from cosmetic Botox?
The Botox used for chronic migraines is exactly the same product as the Botox used for cosmetic purposes. The difference lies in where it’s injected and the volume that’s required.
How much does it cost?
The cost of treatment varies depending on your location and how many units of Botox are required. As a general rule of thumb, you can expect to pay $300-$1,000 or more for a single treatment. Given that the results only last about 12 weeks, the cost can quickly add up.
Will my insurance cover the treatment?
Chronic migraines are an approved indication for Botox, so many health insurers will help cover the cost of treatment. Given most insurance providers consider Botox to be second-line therapy, they may insist that you try other preventative treatments before they’ll cover the cost of Botox injections.
Takeaway
Botox is an excellent treatment for patients whose chronic migraines have not responded to other therapies. It may take some time before you see results, but most patients agree that the eventual pain relief is well worth the wait.
Find a Botox provider near you
When it comes to finding a provider, ideally you should look for a physician who not only has experience with Botox but is also familiar with treating chronic migraine headaches. Our medical review team will help address your concerns and provide appropriate recommendations.