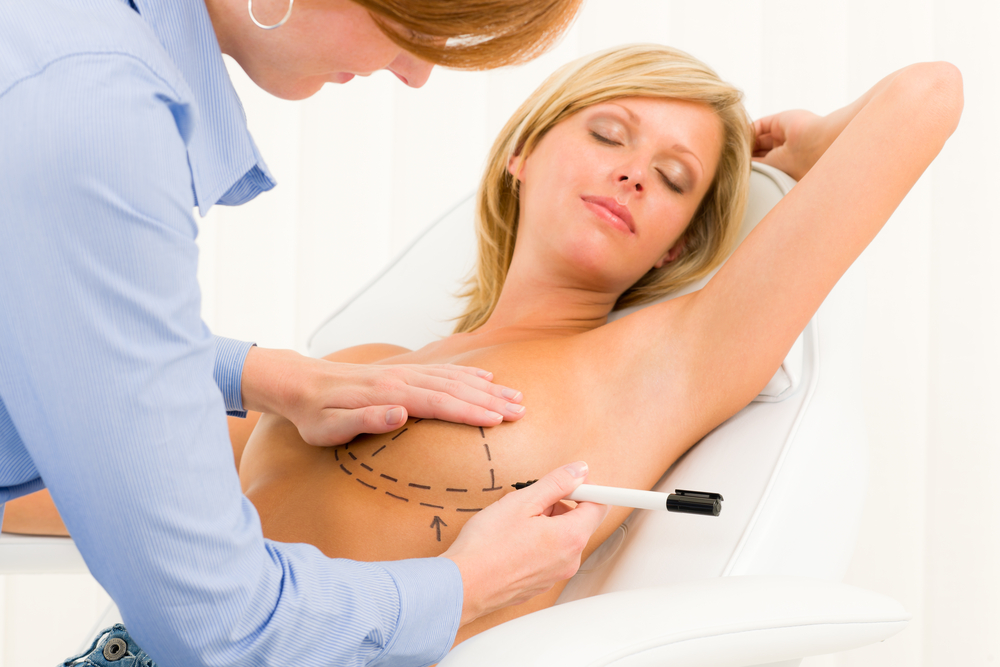
What is a breast augmentation?
A breast augmentation is a surgical procedure performed to increase the size and volume of the breasts, either by inserting implants under the breast tissue, or by grafting fat harvested from other parts of the body into the breast tissue, itself.
Breast augmentation with breast implants is by far the most popular method.
Is it a popular procedure?
There were 300,378 breast augmentations performed in the United States in 2017, making it the most popular cosmetic surgical procedure.
Indications
- Primary macromastia – enhancement of small or underdeveloped breasts
- Secondary macromastia – restoration of volume loss in the breasts due to the effects of weight loss or pregnancy
- Improvement for significant breast size asymmetry
- Lift for small to moderate degree of breast sagging
Who is a good candidate for breast augmentation surgery?
- General good health
- Nonsmokers; it is strongly recommended that smokers stop smoking 4 weeks before surgery and 4 weeks after surgery to minimize the risks of complications
- Contraindicated with medical conditions that may increase the risk of complications during surgery or the recovery period
- uncontrolled high blood pressure
- uncontrolled diabetes
- Weight stable with BMI (body mass index) ideally less than 30
Types of breast implants
There are two categories of breast implants based upon their fill material: Saline and Silicone
| Saline | Silicone | |
|---|---|---|
| Contents | Silicone shell filled with saline (salt water) | Silicone shell filled with silicone gel |
| Min. age per FDA | 18 years of age | 22 years of age |
| Implant filling | Implants come empty and are filled at time of surgery to different ranges | Implants come prefilled with set amounts |
| Appearance | Fuller, more projecting | Softer, less projecting, more natural |
| Rippling | Higher risk | Lower risk |
| What happens if it ruptures? | Breast gets visibly smaller as implant deflates | You may not see any change in size or shape of breast |
| Rupture surveillance | None | MRI after first 3 years, then MRI after every 2 years |
| Replacement | No need to replace implants unless they deflate | Replace every 10-15 years |
| Avg. cost | $3,268 | $3,618 |
Preparation
Routine blood work is generally required preoperatively to check basic blood levels to make sure a patient is medically stable to undergo the procedure.
Depending upon the patient’s age, a chest X-Ray and EKG may be required as well. Medical clearance may be required if there are any known medical conditions that can affect the surgery or the recovery.
Patients are required to stop all food and drink at least 6-8 hours before the surgery. Some centers require no food or drink after midnight the night before the surgery.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia for breast augmentation may be in the form of general anesthesia or sedation.
With general anesthesia, which is more commonly performed for breast augmentation, the patient is completely asleep and a breathing tube is either placed in the throat or in the back of the mouth.
With sedation (also known as “twilight”), the patient is not completely asleep, but will not be aware of any part of the procedure that is taking place. No breathing tube is used with sedation.
Incision types
Inframammary Crease
- Lower border of the breast
- Most common
Periareolar
- Lower border of the areola
- Increased incidence of infection, capsular contracture, changes in sensation to areolas, decreased ability to breast feed
Axillary (Armpit)
- Mostly used for saline implants and smaller silicone implants
- Increased risk of implant malposition
Belly button (TUBA – transumbilical breast augmentation)
- Limited to saline implants
- Increased risk of implant malposition
What should I expect during recovery?
- One should expect to be home from work or school for one week following a breast augmentation, avoiding activities such as driving or lifting.
- Recovery from implants placed under the muscle may be more uncomfortable as compared with the recovery from implants placed over the muscle.
- Postoperative discomfort may be alleviated with low dose valium (2mg – 4mg every 6 hours) or Exparel liposomal bupivacaine injected by your surgeon at the time of the surgery. Exparel has been shown to dramatically reduce postoperative discomfort for up to 3 days after surgery.
- Sutures may be dissolvable or removable. Removable sutures are usually taken out at 10-14 days.
- A postoperative bra or sports bra should be worn for 4-6 weeks.
- Massage to the breasts should be started in the first week to help the implants drop into position. Note that saline implants require more massage than silicone implants.
- You should avoid sleeping on your belly or sides for 4-6 weeks.
- Avoid lifting anything over 10 lbs. for 4-6 weeks.
- You may resume exercising after the 2 weeks. You should avoid any isolated chest exercises for 3 months.
- Scar regimens (scar cream, silicone sheeting, etc.) should be started at 4-6 weeks after surgery, once the incisions are healed and free of any scabbing.
» Learn more about what to expect during breast augmentation recovery
What are the risks of a breast augmentation?
Although breast augmentation is a very safe procedure when performed by a skilled surgeon, there are risks associated with the procedure. These include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Wound breakdown
- Asymmetry
- Implant malposition
- Changes/loss of sensation to the breast and/or nipple area
- Implants too large/too small
- Capsular contracture – excessive scar tissue around the implant distorts the implant and may cause pain
- Excessive/hypertrophic scarring
Links with breast implants and other diseases
Although it has been shown that women who have breast implants are more likely to detect breast cancer, breast implants have not been linked as a cause of breast cancer.
Women with textured surfaced breast implants (either saline-filled or silicone filled) have a low but increased risk of developing breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).
Breast implants have not been shown to be a cause of any known systemic autoimmune diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, or Sjogren’s syndrome.
What is Breast Implant Illness?
Breast Implant Illness (BII) is a name given to cover a range of symptoms that have been described by women who have undergone breast augmentation with either saline or silicone implants.
Symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Aches
- Pains
- Brain fog
- Depression
- Panic attacks
- Short term memory loss
- Hair Loss
- Changes in skin
Is has been postulated that these symptoms are due to elevated IgE serum antibodies in response to the silicone present in both saline-filled and silicone-filled breast implants. A scientific link has not been established.
Picking a surgeon for breast augmentation
When selecting a surgeon to perform a breast augmentation, it is important to select an experienced practitioner to minimize the risk of complications and maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
Surgeons performing the procedure should be board certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery, the American Board of Medical Specialties accredited member board for plastic surgeons.
The surgeon you select should only perform the procedure at a hospital, an accredited surgical center, or an accredited office-based operating room.
Fat grafting
Fat grafting as a means of breast augmentation far less popular as compared with implants as it is limited to those who have sufficient fat to graft and can only increase the breast by one cup size.
Breast enlargement pills
Pills and supplements that claim to increase the size of the breasts typically consist of herbal supplements that mimic the effects of estrogen. Short term, they may enhance the size of the breasts by promoting water retention. Longer term, they may stimulate estrogen receptors within the breast tissue to increase breast tissue growth. There is no proof that any of these pills or supplements show clinically significant enlargement of breast size, and they may actually be harmful to your health.