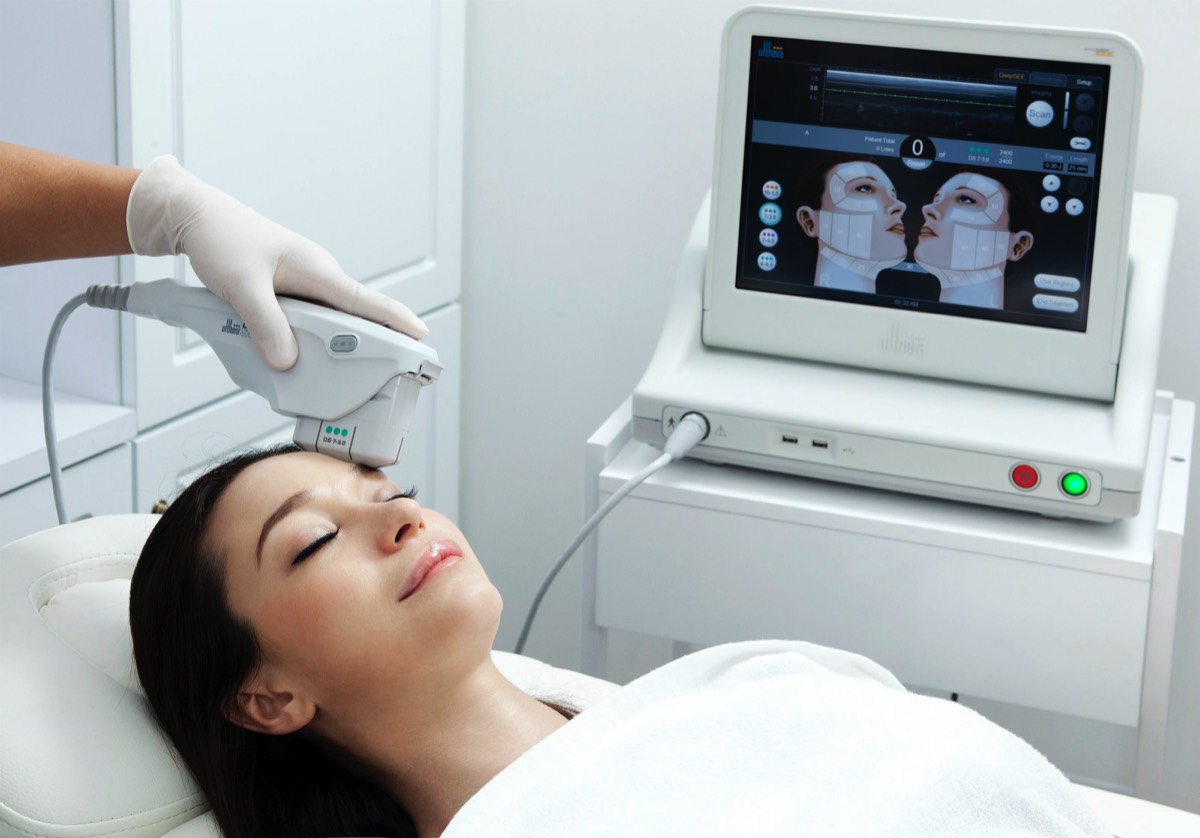
Carbon dioxide therapy can be used to treat many types of skin blemishes, as well as stubborn fat and cellulite.
An adult in good health will inhale several gases, in particular large amounts of oxygen, 12 to 20 times per minute. This is quickly followed by exhaling gases, most notably carbon dioxide. While it’s easy to jump to the conclusion that carbon dioxide isn’t needed in our bodies, it actually plays a vital role.
Carbon dioxide tells the body when it requires additional oxygen. This signalling role is an important part of making the bodywork, and the key element to carboxytherapy.
What Is Carboxytherapy?
Carboxytherapy, also called carbon dioxide therapy, is a process during which carbon dioxide (CO₂) is injected directly into the skin to promote blood flow and increase skin elasticity. Many practitioners offer this treatment as a non-invasive alternative to liposuction and anti-aging procedures like facelifts.
CO₂ has been used to improve blood flow since at least 1932, when it was employed by French practitioners to treat patients with narrow arteries.
While the exact procedure for carboxytherapy varies depending on the treated area and the clinic performing the procedure, the basic elements remain the same. A small needle is used to deliver the medical grade CO₂ to the desired area. A machine then regulates the flow of gas into the skin through a plastic tube attached to the syringe, assuring a steady, measured stream of CO₂.
Several injections are often needed to distribute the gas evenly in the treated area. These injections are generally made between 10 and 13 millimetres into the body, but can vary depending on the area. The treatment takes between 15 and 30 minutes, with most patients only reporting mild discomfort from the procedure.
Uses and Benefits of Carbon Dioxide Treatments
Modern aesthetic uses for carboxytherapy tend to focus on three aspects: lessening the appearance of skin blemishes, improving dark circles around the eyes, and reducing localized fat.
Stretch Marks and Blemishes
Carbon dioxide therapy can be used to treat many forms of skin blemishes, most notably stretch marks, scars, and wrinkles.
Stretch marks are caused by rapid weight changes, pregnancy, and adolescent growth spurts. Essentially, they are blemishes that appear when changes to the body happen too quickly for the skin to keep up naturally. The middle layer in the skin tears, revealing the blood vessels present in deeper layers of the skin.
This breakdown in the body’s natural collagen can be improved through carboxytherapy, as the procedure aids in speeding the natural healing process.
Scar tissue on the skin, the result of injury or acne, tends to fade slowly over the course of several years. While carboxytherapy cannot heal scar tissue, it can increase the flow of oxygen to the area, helping the scar blend in more seamlessly. The procedure can speed the fading process of a scar by months or even years, depending on the scar’s location and its severity.
One of the most cited reasons for undergoing cosmetic procedures is to ward off the visual signs of aging. Carboxytherapy improves the elasticity of the skin, which in turn helps smooth out wrinkled areas. The treatment is primarily limited to smaller wrinkles with only minor amounts of skin sagging. This makes it ideal for younger patients with the earliest signs of wrinkles.
When removing deeper wrinkles, carboxytherapy can be used to supplement more drastic skin tightening procedures like facelifts.
Under Eye Circles
Many people suffer from dark patches under their eyes that give them a worn out or tired look. In particularly bad cases, these circles can look like black eyes, bruises, or hemosiderin staining (bruising). These unwanted eyesores are caused by either broken blood vessels in the periorbital skin, or poor circulation in the area.
The periorbital skin is only 0.5 millimetres thick, roughly a quarter of the thickness of the skin on most of the other parts of the body. This is why the area is more prone to darkening than others. Carboxytherapy can help improve circulation in the area and deliver a more alert appearance.
When carbon dioxide therapy is applied to the eyelids, the area will take on a swollen appearance. This quickly fades however, as the gas dissipates in the minutes following the procedure.
After a series of injections, the results last for roughly six months.
Localized Fat Reduction
Certain areas, such as thighs and under the chin, store more fat cells than the rest of the body. This can give an otherwise thin person a heftier appearance. Localized carbon dioxide therapy will help the body burn this fat at a quicker rate, especially as a supplement to regular exercise.
Cellulite occurs when body fat makes its way through the connective tissue beneath the skin, creating a lumpy appearance. This tends to occur in fat rich areas like the legs and buttocks. While anyone can have cellulite, it is far more common in women. Roughly 90 per cent of women over 30 have cellulite.
From homemade remedies to cosmetic procedures, there are many options for cellulite reduction, but carboxytherapy offers a targeted approach that is both quick and relatively painless. Carbon dioxide helps to increase blood flow to connective tissue, which in turn reduces the appearance of cellulite.
For both cellulite and general localized fat, the procedure occurs over the course of roughly six injections. One injection is made per week to maximize the efficiency of the procedure, and results begin to appear within days of the first treatment.
Unconventional Uses
Due to its simplicity and general safety, the procedure is applied to a variety of cases that extend beyond its traditional use. Certain clinics offer carbon dioxide therapy to either bolster or replace common hair rejuvenation techniques. Injections can be as frequent as once a month in order to maintain the results of this hair loss solution.
Carboxytherapy has also been used by some practitioners to treat erectile dysfunction resulting from poor circulation.
In its liquid form, CO₂ is applied topically for many of the same reasons people generally seek out carboxytherapy. Studies by the University of Oklahoma have shown that topical use of CO₂ can double blood flow to skin.
Recovery
As a quick, noninvasive, and zero down-time procedure, carboxytherapy is a triple threat. The chances of serious side effects from typical carbon dioxide therapy are essentially nonexistent when performed by a trained professional. The most common side effect of the procedure is mild bruising at the site of injection which typically fades within a matter of days.
Recovery takes a matter of hours, if not minutes, as the gas only needs time to disperse. In the hours following certain types of carboxytherapy, submerging the body in water is not recommended.
While this procedure will not deliver results of the same caliber as more invasive treatments, it still offers significant change with a smaller investment of time, something many will find very appealing.